Automation and Robotics: Robot Crane
Project Goal
We have to develop a robotic crane which can be operated remotely. This robotic crane is capable of operating in a predefined working area, picking up and lowering down an object freely. To achieve the goal, we have to design the robot hardware (at least three degree of freedom: slewing, trolley forward and backward, hoisting) and also a software that can control the crane to perform the tasks smoothly. The user can control the robotic crane by using mouse or keyboard to lift and lower the object. In this project, we also need to develop “fine motion” operation (column’s bottom cannot move during the lifting operation).
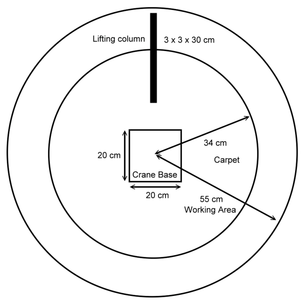
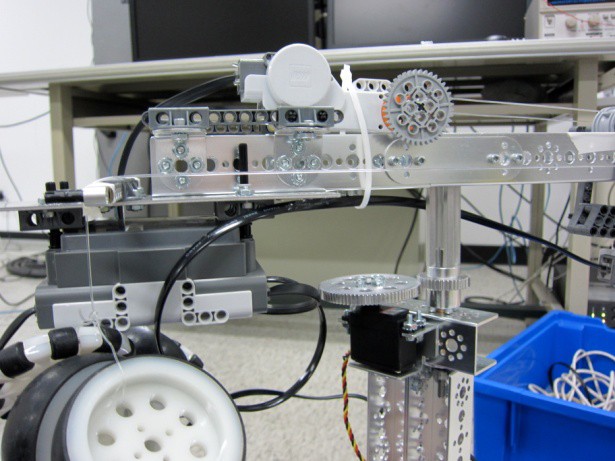
Mechanism Design
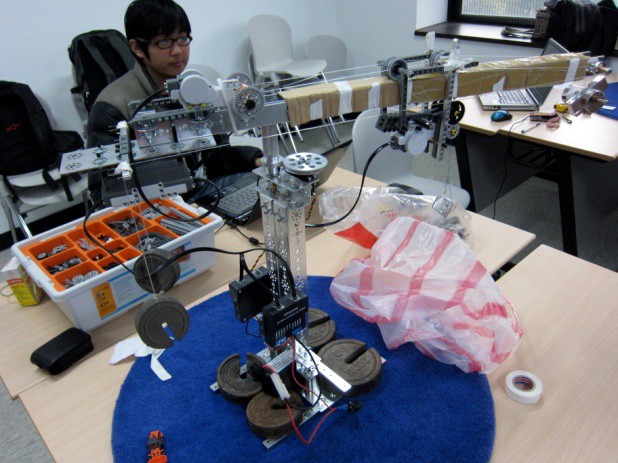
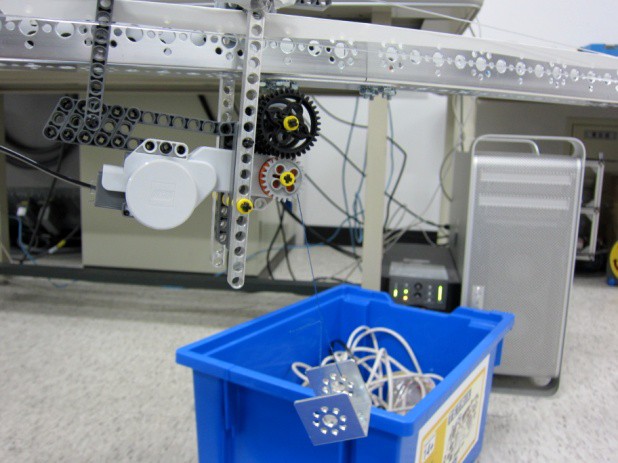
We used Lego Mindstorm NXT and TETRIX to build our robotic crane. There are three degrees-of-freedom in the robot, i.e., rotation, translation, and lifting. First, the rotation mechanism utilizes a servo motor and gears to rotate the jib clockwisely and conterclockwisely for up to 180 degrees. Next, the translation mechanism uses a cable and Lego motor to drag the trolley to move backward. Several wheels are placed at the back of the jib as counterweights to provide forward movement. In the final version, we change the wheels to two weights as counterweights. Finally, the lifting mechanism uses a Lego motor to drag the cable to lift the component.



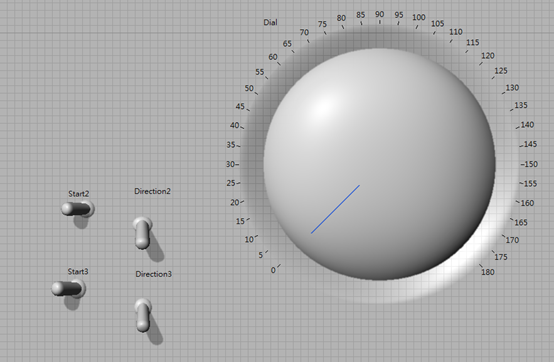
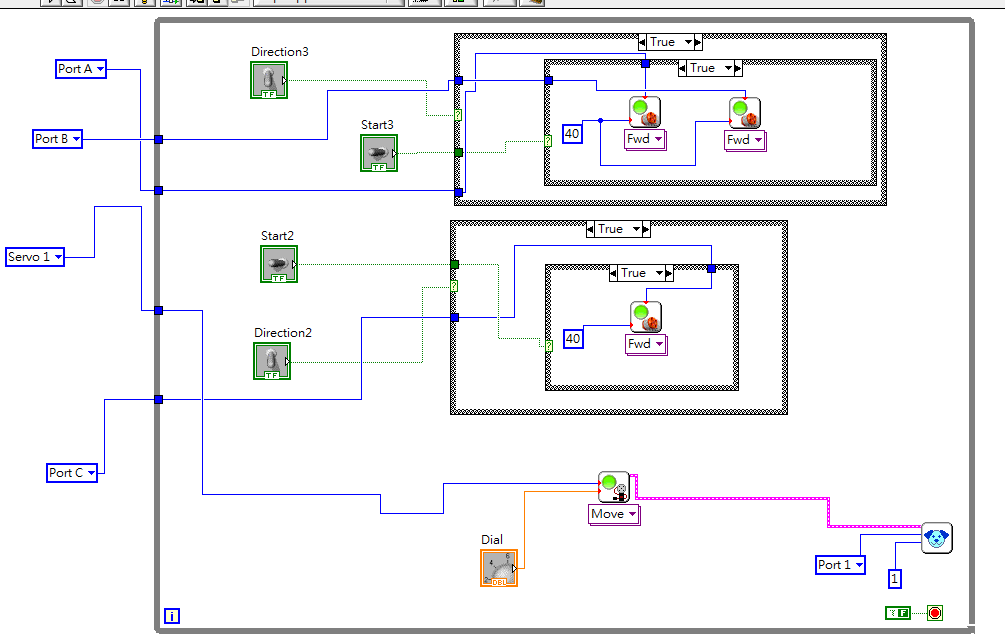
UI Design
For the user interface and robot programming, we use LabVIEW to develop the control panel and control the robotic crane. The interface is discussed as follow:
- The knob is used to control the slewing angle, i.e., the servo motor angle.
- Start2 and direction2 switches are used to control the trolley forward and backward.
- Start3 and direction3 swtiches are used to control the hoisting up and down.