RAS: Robotic Assembly System for Steel Structure
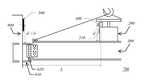
This research focuses on a long-lasting yet critical problem in the erection assembly of steel structures. In the current state of practice, steel workers need to stand on the unfinished structure to assist the assembly of structural elements manually. They must grab the wire under the rigging elements and align the bolting holes between the moving and fixed elements. These works are usually performed in high places, which are very challenging and unsafe. Therefore, we developed a robotic assembly system (RAS) that remove workers from the dangerous spot and perform the assembly tasks semi-automatically. The RAS consists of four modules: rotation, alignment, bolting, and unloading module. First, the rotation module is a mechanism box equipped with a flywheel on the top of the rigging beam aiming to rotate the beam to the assembly angle. The operator controls the flywheel at the remote location.
Second, the alignment module is divided into two stages: vertical alignment and horizontal alignment. The vertical alignment is used to ensure the rigging beam is at the right altitude. We use a camera to detect a marker on the column and a light signal to inform the operator that the beam has reached the target altitude. The horizontal alignment is used to ensure the beam is at the assembly position, which is achieved by a specially designed beam shape. The shape of the beam flange is parallelogram so the beam can be smoothly trolled to the assembly position. Third, the bolting module is used to assemble the beam. We add an additional plug hole above each bolt hole. With the newly designed bolt, it can plug in and slide to the bolt hole. Finally, the unloading module is used to unload the rigging cable and the RAS. We use a pin mechanism for beam-hook connection and attach to RAS, so it can be unplugged by motors easily.
The system was implemented in a scaled-experiment construction site and compared with the traditional process. The results showed that the RAS can reduce the operation time by 86% and operate without human workers nearby. In conclusion, we develop a robotic assembly system that can help reduce the accidental falls of the steel beam assembly process. The RAS fits the current erection process and can be broadly introduced to existing construction sites.